Meet the Cell
The assembly
Your body is made up of billions of micro and nano "bricks" called cells.
Each cell is a living organism that eats, breathes, excretes and performs specific tasks as individuals in a given society!
Billions of these organise together make you "be" you, or make your body if you are smart enough...
Identical cells group together to form tissues, such as bone or muscle tissue.
Then the tissues group together to form the organs, which are the main separate elements that make up the body.
All this is possible only with these microscopic cells.
Let's see what the bulk of the cells are made of...
Generic cell
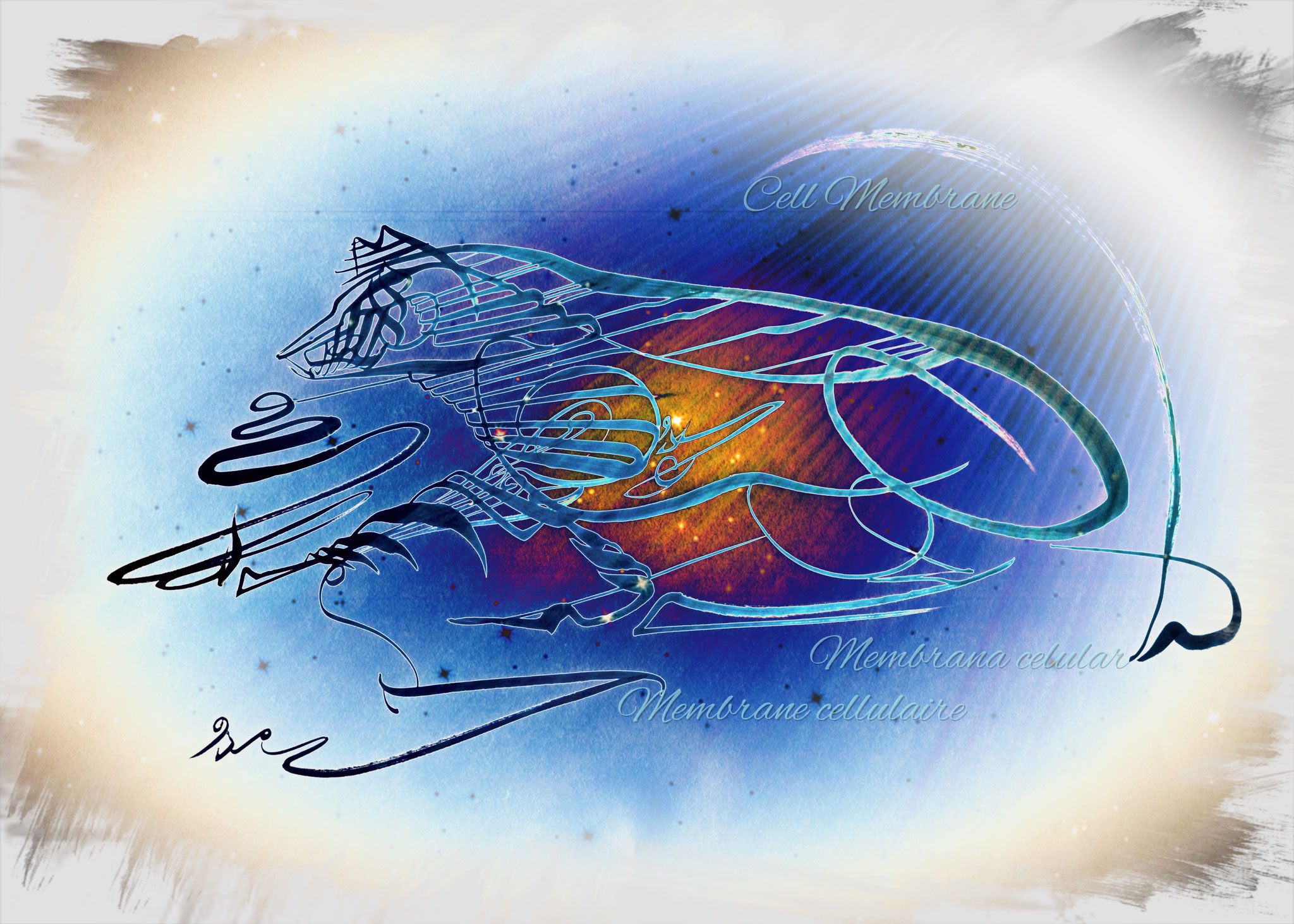
Cellular membrane
The cell membrane is the skin of the cell.
It is a bag filled with an aqueous substance called cytoplasm.
Lysosomes
These are bags filled with chemicals that digest unwanted or worn out particles from the cell.
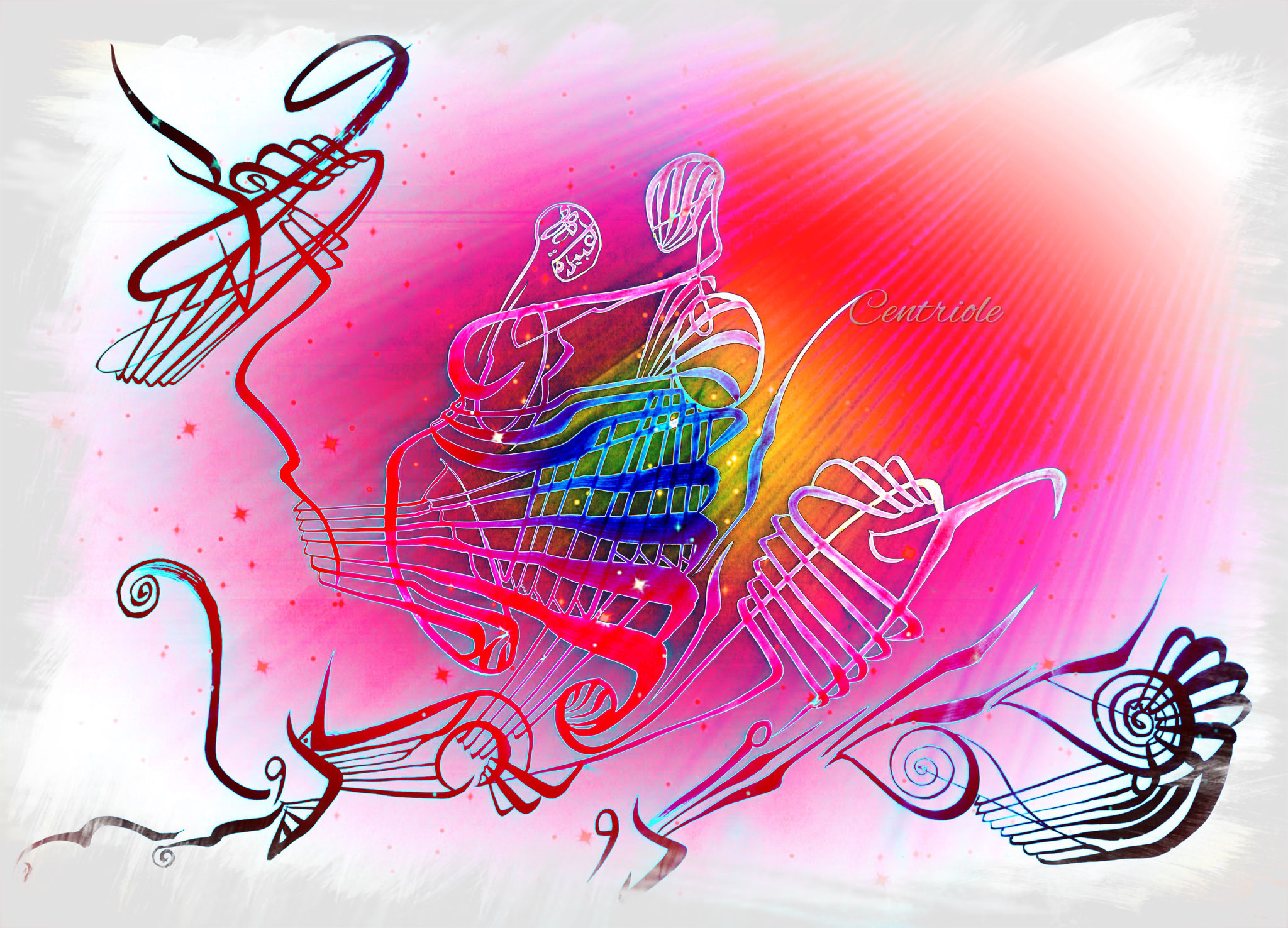
Centrioles
Cylindrical organ close to the nucleus in animal cells, in pairs and involved in the development of "spinale fibers" in cell division.
The core
The control center of the cell.
The nucleus contains the chromosomes, an x-shaped DNA chain.
The structure of the DNA is sinusoidal in shape as for the synusoido-eliptic movement of the Earth around the sun!
DNA carries genes, a code that determines the structure and growth of the body.
Endoplasmic reticulum
It is a network of membrane tubules, often interconnected, dispersed throughout the cytoplasm.
Its membrane, which alone accounts for more than half of the cellular membrane system, is in contact with the nucleus.
Golgie apparel
An organism that allows the synthesis and modification of certain proteins and certain lipids by adding, for example, sugar, phosphate or sulphate.
Thanks to these modifications, the molecules will be able to become active.
Participating in particular in the renewal of membranes and in the storage of cellular calcium.
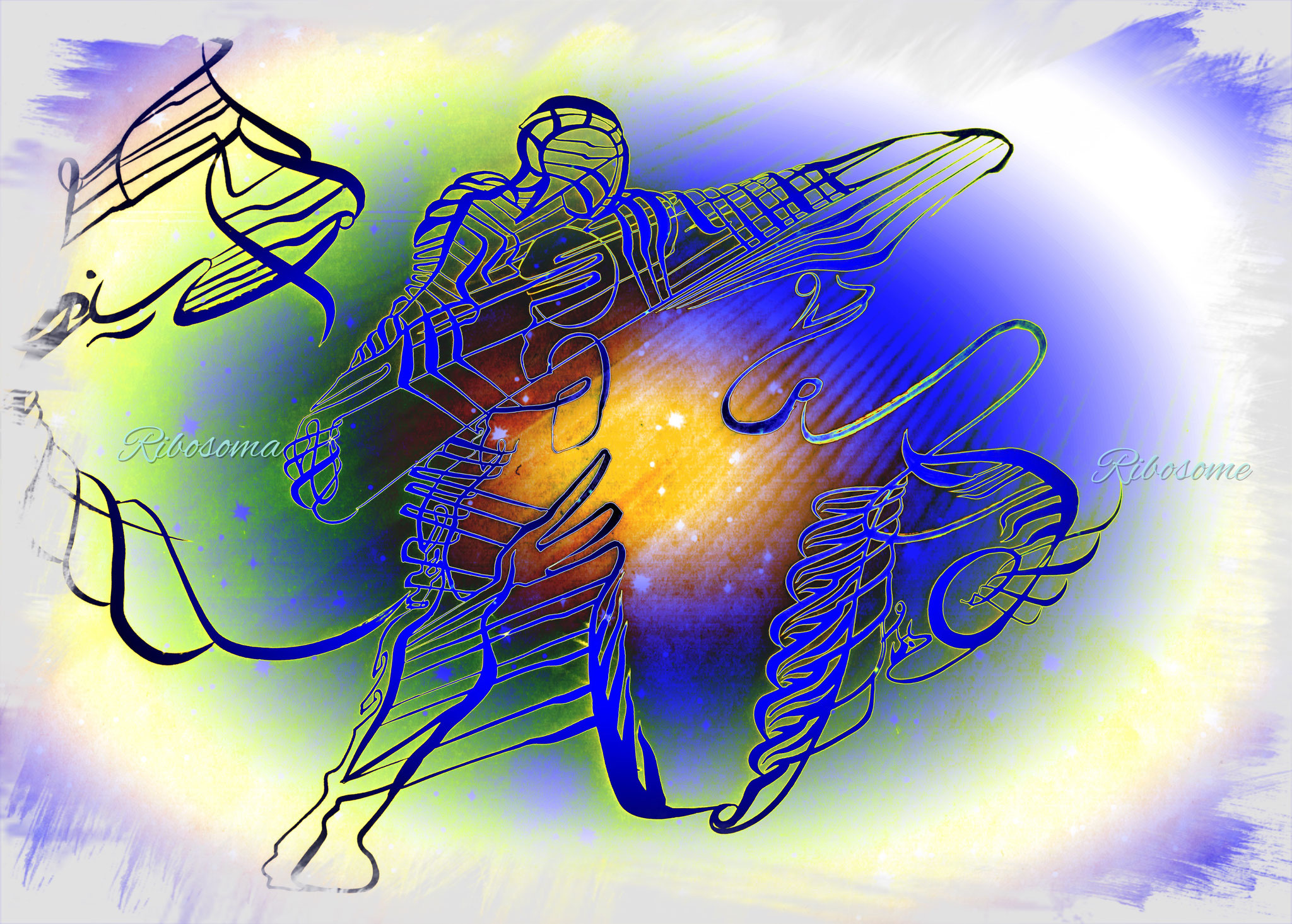
Ribosomes
A cellular organism whose role is to decipher the mRNA signal to synthesize proteins, the basic ingredient of the skin, muscles, bones, and most of the body.
The mRNA is a duplication of a DNA strand.
The ribosome consists of two units.
The first unit reads the code written on the mRNA.
The second unit is responsible for aggregating the amino acids together to form a protein.
The ribosome is translator and transcriptor of information!
When a cell becomes two!
Our billion cells live, do their specific tasks and die.
Every minute, millions of cells die and are replaced in the body, without our couscious participation, in a "self-managed" way!
Cells duplicate accurately from DNA in the nucleus.
This process is called Mitosis, where the mother cell splits into two, forming two identical "daughter" cells!
Different cell types
Nerve cells
Present throughout the body, nerve cells, also called neurons, transmit electrical messages between the brain and muscles, glands or other neurons.
Nerve cells would be involved in every one of your movements, thoughts, or sensations!
Muscle cells
They are the only cells capable of contracting, and becoming smaller or wider.
It is this property that makes movement possible.
Red blood cell
Also known as "erythrocytes", the redblood cells are "doghnuts" shaped cells responsible in particular for the transport of oxygen throughout the body.
They are formed in the bone marrow, in the center of the bones.
Skin cell
The skin we see on our bodies consists of 20to 30 layers of predominantly dead cells
They compacted to provide perfect protection against extreme temperatures, loss of water or injury.
Fat cells
These cells store nutrients and oils, insulate against heat loss and protect the organs like the brain, lungs and heart.
The nucleus of a lipid cell is compressed on the side of the cell membrane leaving the remainder of the vacant space to store a drop of fat or oil!
White globule
Also called "leukocytes", and mostly formed in the bone marrow.
These cells get rid of bacteria, viruses and microscopic germs that cause disease and infection.
Phagocytosis is the name given to the process of absorption of the germ and its elimination outside the body.
The used white blood cells leave the body in the pus or by forming a crust or being filtered through the kidneys and eliminated in the urine.
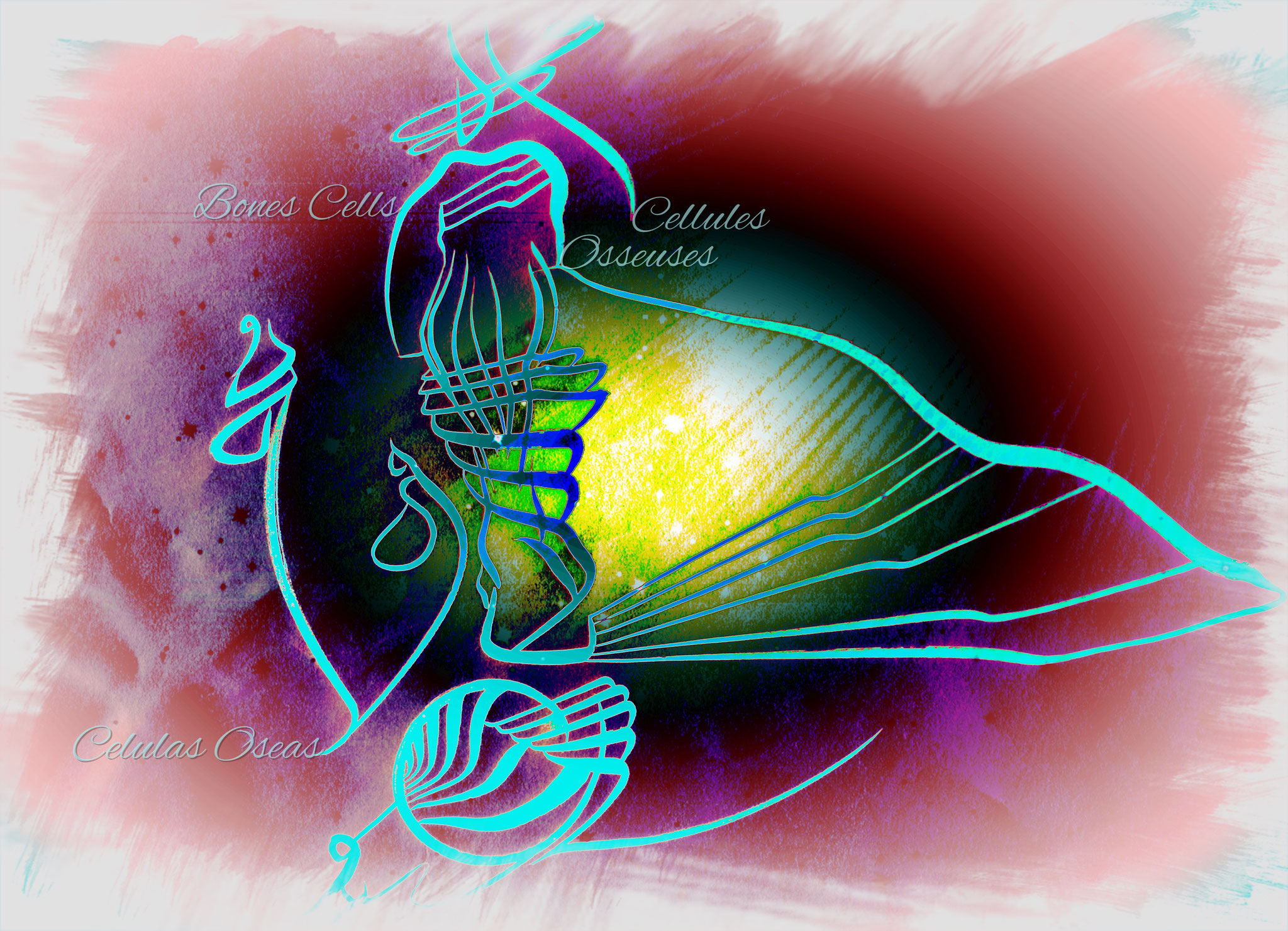
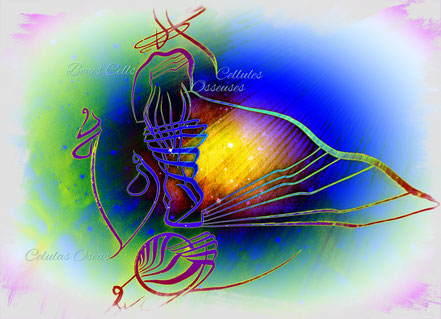
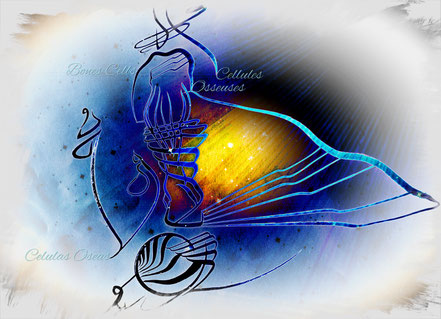
Bone cell
The outermost layer of your bones are made of firmly compacted cells ring sets.
These circles grow outward like a tree truck making the bone layers very solid.
Ovule
The egg contains the genes in its nucleus, and is the largest cell in the body.
The mature egg follows its way through the fallopian tubes to meet the spermatozoa.
The two gamètes would then combine their genetic codes to form a new embryo, which will give the future baby.
Spermatozoon
Spermatozoa are typically designed for movement!
Its head is covered with a helmet intended to pierce the cellular membrane of the ovule.
Genes are locked in the nucleus, they make up the other half of the code that will determine what the baby will look like or how the body will function.